Decoding the Mechanics of High-Performance Processors
High-performance processors are the core engines driving modern computing, from the smallest digital devices to the most complex systems. These intricate pieces of hardware are responsible for executing instructions, processing data, and enabling the advanced functionalities we rely on daily. Understanding their fundamental mechanics is key to appreciating the technological advancements that shape our digital world and the ongoing innovation in electronics.
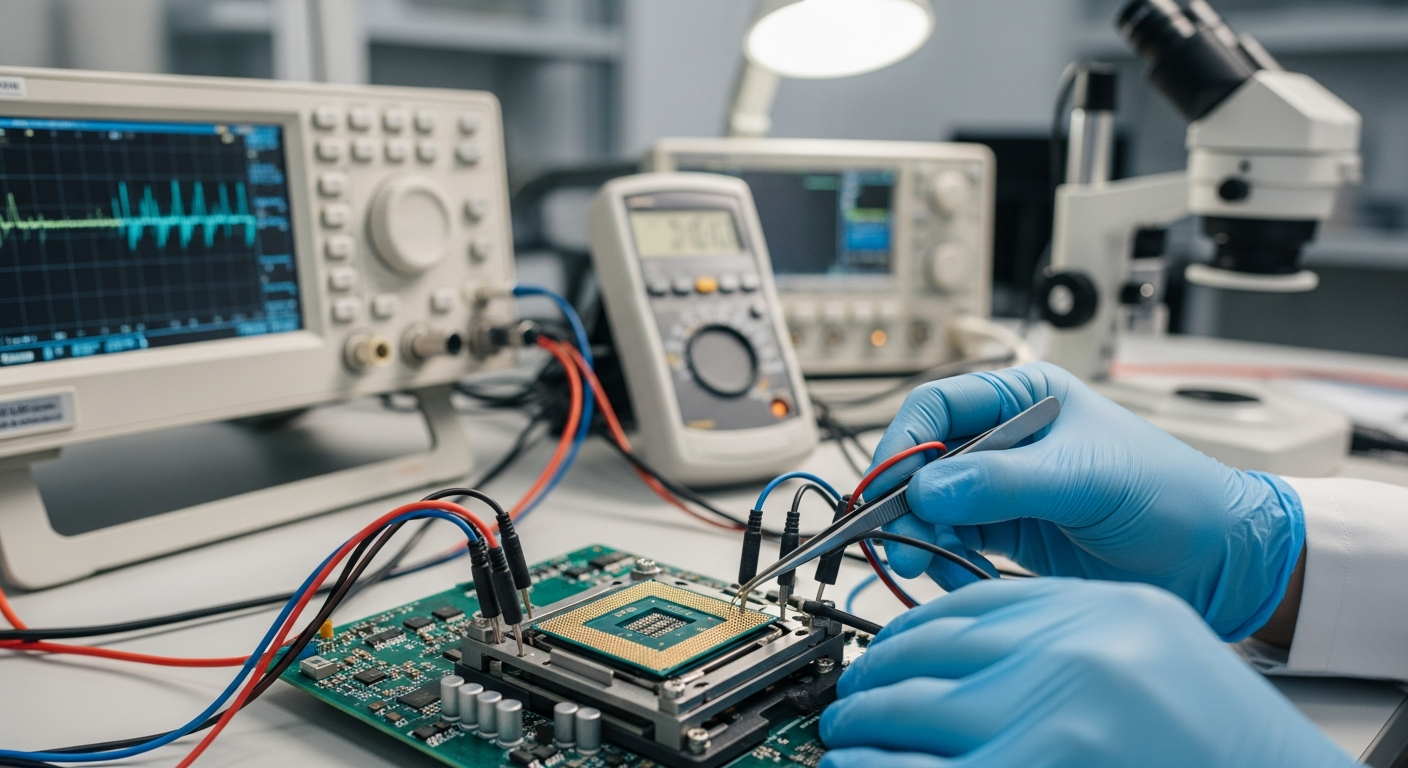
The central processing unit, or CPU, is often referred to as the brain of any computing device. Its primary function is to interpret and execute the instructions that make up computer programs. This involves performing arithmetic, logical, and input/output operations. A high-performance processor achieves its speed and efficiency through a combination of sophisticated architectural designs, advanced materials, and precise manufacturing techniques, constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible in digital technology.
The Role of Processors in Modern Computing
Processors are foundational to nearly all modern computing tasks. They orchestrate the flow of data, manage memory, and execute complex algorithms that power digital experiences. From browsing the web on mobile phones to running intensive simulations on laptops, the processor’s capability directly impacts performance. It’s the silent workhorse that translates user commands into actions, enabling seamless interaction with devices and systems across various platforms.
How Hardware Components Interact for Optimal Performance
Effective hardware integration is crucial for maximizing processor performance. A processor doesn’t work in isolation; it collaborates closely with other components like RAM (Random Access Memory), storage devices, and the graphics processing unit (GPU). The speed at which data can be moved between these elements, often facilitated by a high-speed bus, significantly influences the overall system responsiveness and capability. Efficient electronics design ensures these interactions are optimized.
Innovation and the Evolution of Processor Circuits
The relentless pursuit of innovation is evident in the continuous evolution of processor design. Modern processors feature billions of transistors, tiny electronic switches arranged into complex circuits. Advances in semiconductor manufacturing, such as smaller process nodes, allow more transistors to be packed into a smaller area, leading to increased processing power and energy efficiency. This constant refinement drives the development of faster and more capable gadgets.
Powering Digital Devices and Complex Systems
High-performance processors are integral to a vast array of digital devices and systems. Beyond personal computers, they are found in servers that power the internet, embedded systems controlling industrial automation, and specialized devices for scientific research. Their ability to handle multiple tasks concurrently and process vast amounts of data makes them indispensable for the complex operations required by today’s interconnected world, underpinning virtually all technology.
Understanding Processor Performance and Automation
Processor performance is measured by several metrics, including clock speed, core count, and cache size. Clock speed indicates how many cycles per second a core can execute, while more cores allow for parallel processing of multiple tasks. Cache memory provides quick access to frequently used data, reducing latency. These factors collectively contribute to a processor’s ability to handle demanding applications and facilitate advanced automation tasks, making processes more efficient and responsive across various industries.
Key Components and the Broader Electronics Landscape
Inside a processor, several key components work in concert. These include the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) for calculations, control units for instruction management, and various levels of cache memory. The intricate design of these elements, fabricated on a silicon wafer, represents a pinnacle of modern electronics manufacturing. As part of a larger networking ecosystem, processors enable communication and data exchange, forming the backbone of interconnected digital infrastructure and driving progress in countless fields.






