Unraveling the Mysteries of Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
The world of auto engineering is an ever-evolving landscape, brimming with advancements that push the boundaries of efficiency and performance. One such technology that has significantly altered the dynamics of modern cars is Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT). Though not a recent innovation, it's seeing a resurgence in popularity due to its unique advantages in fuel efficiency and smooth driving experience. This article will delve into the workings of CVT, tracing its development, present use, and future implications.
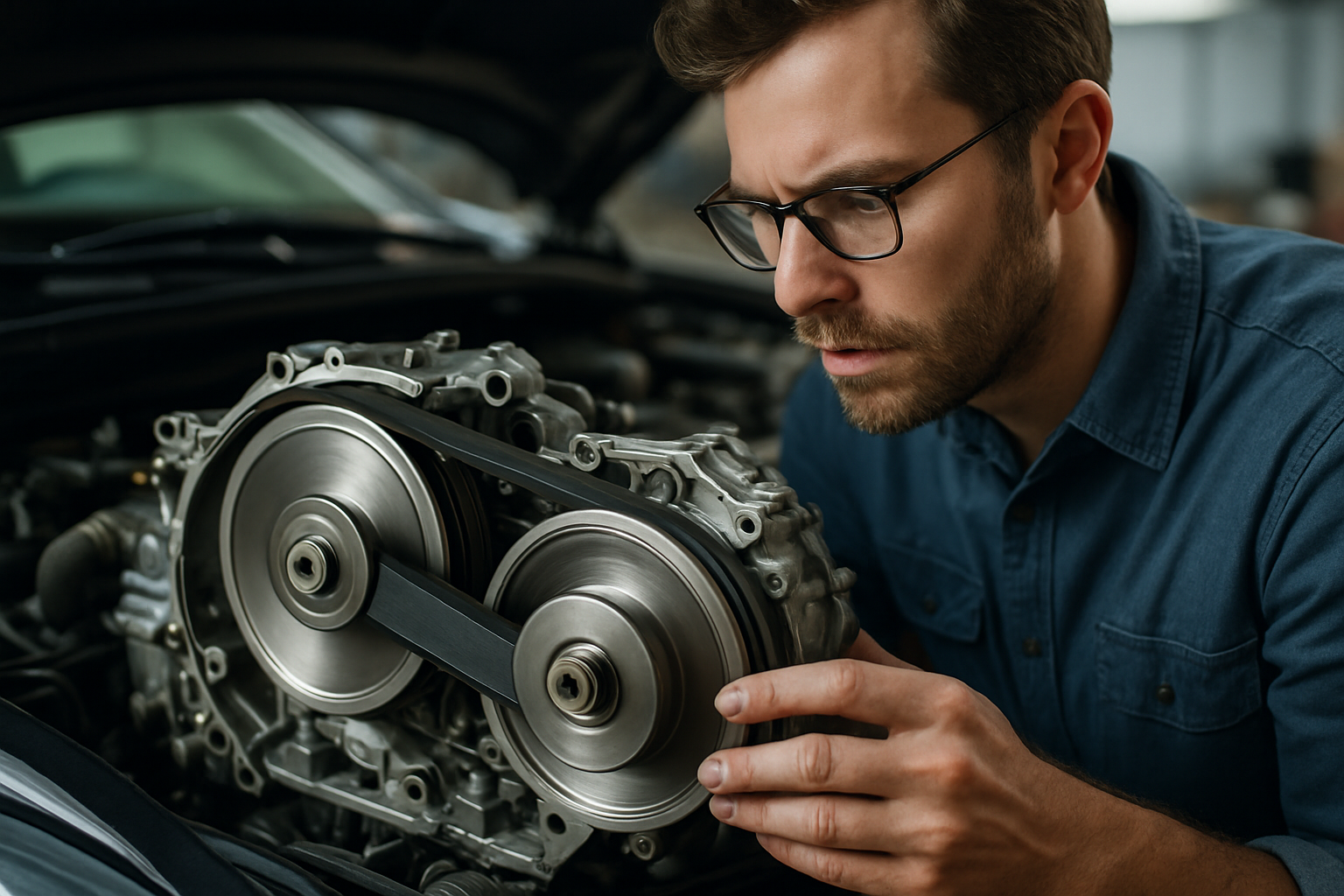

A Glimpse into the Past: CVT’s Origins
CVT is not a new kid on the block. In fact, its inception can be traced back to the late 19th century, when inventor Milton Reeves used it in his sawmilling and car manufacturing operations. However, it was not until the 1950s that CVT started gaining momentum in the automotive industry. DAF, a Dutch automobile manufacturer, was the first to introduce CVT in passenger cars. Despite early skepticism due to its perceived mechanical complexity, CVT became a popular choice for improving fuel efficiency and enhancing driving comfort.
How CVT Works: Simplifying Complexity
Understanding CVT requires a shift from conventional gears-and-clutches thinking. Instead of using fixed gear ratios, CVT employs two pulleys connected by a belt or chain, with one pulley attached to the engine and the other to the transmission. The diameters of these pulleys can change, creating an infinite range of gear ratios, hence the name ‘Continuously Variable.’ This mechanism allows for smoother acceleration and optimal engine performance at varying speeds.
Riding the Trend: CVT’s Growing Popularity
In the quest for fuel efficiency and a smoother driving experience, many car manufacturers have turned to CVT. Renowned automakers like Nissan, Honda, and Subaru have adopted CVT in several of their models, citing its advantages in fuel economy and seamless acceleration. This growing preference for CVT is indicative of a larger industry trend towards maximizing efficiency without compromising performance.
The Implications of CVT: Pros and Cons
Like any technology, CVT comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. On the plus side, CVTs offer improved fuel efficiency and a smoother driving experience due to the absence of gear shifts. However, CVTs also have some drawbacks. They can be expensive to repair or replace due to their complex design. Additionally, some drivers note a distinct ‘rubber band’ feel during acceleration, a characteristic of CVT that may not be to everyone’s liking.
Looking Ahead: The Future of CVT
Despite these challenges, the future of CVT seems promising. With advancements in technology and material science, the drawbacks of CVTs are being steadily mitigated. The ongoing research and development in this field are likely to make CVTs an even more attractive option for manufacturers looking to improve fuel efficiency and driving comfort.
In conclusion, Continuously Variable Transmission is a compelling testament to the innovative spirit of the automotive industry. Its unique combination of fuel efficiency and smooth acceleration makes it a fascinating subject for anyone interested in the future of automotive technology. Despite some challenges, the potential of CVT is immense and holds promise for the future. As we delve deeper into the realm of vehicle technology, it’s clear that the road to innovation is indeed continuously variable.