"Untangling the Mystery of Holographic Storage: The Future of Data Preservation"
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, the hunt for efficient and long-lasting data storage solutions is an ongoing saga. One promising development that has captured the imagination of tech enthusiasts is holographic storage—a futuristic concept that promises to revolutionize the way we store and retrieve data.
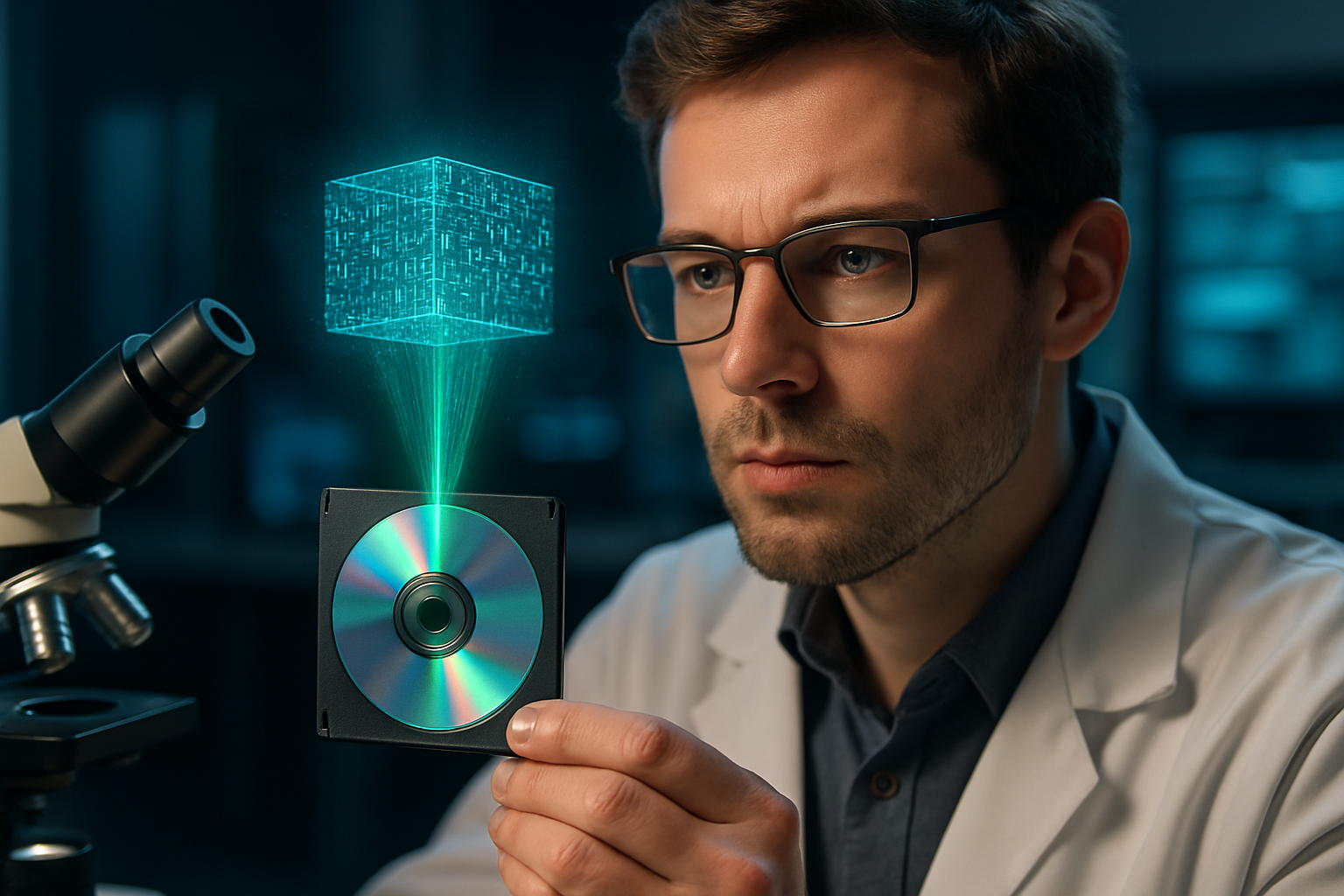

The Making of Holographic Storage: A Historical Overview
Holography, as a concept, was first introduced by a Hungarian-British physicist, Dennis Gabor, in the 1940s. The word ‘holography’ derives from the Greek words ‘holos’ (whole) and ‘graphein’ (write). It refers to the process of capturing light scattered from an object and reconstructing it in a 3D form. However, it wasn’t until the invention of laser technology in the 1960s that holography found practical applications.
Fast-forward a few decades, and the technology evolved to incorporate data storage. In the 2000s, companies like InPhase Technologies began developing holographic storage devices. However, due to technical difficulties and market dynamics, these early attempts did not take off commercially.
Holographic Storage: The Present Scenario
Fast forward to the present day, and holographic storage is once again in the spotlight. The technology is no longer a far-fetched idea as researchers worldwide are making significant strides to bring it to fruition.
Companies like Akonia Holographics, purchased by Apple in 2018, are working on holographic storage and display technologies. Meanwhile, researchers at the University of Cambridge have recently developed a method to store data holographically in subatomic particles, a development which could potentially lead to significant advancements in this field.
The Impact: Storing Data in Three Dimensions
Holographic storage boasts multiple advantages over traditional storage methods. It offers high storage density, as data is stored in three dimensions, not just on the surface of the material. This means that a single disc has the potential to hold terabytes of data.
The technology also promises fast data transfer rates and long-term data preservation. Unlike magnetic storage, which can degrade over time, holographic storage is not susceptible to magnetic fields, heat, or moisture, making it far more durable.
The Price Tag and Market Impact
While it’s hard to estimate the exact cost of holographic storage devices at this early stage, the price is expected to be high initially, given the advanced technology involved. However, as with most tech products, the cost is likely to decrease as the technology matures and competition grows.
The introduction of holographic storage could significantly impact the data storage market. It could provide a solution to the growing demand for high-capacity, durable storage options, especially in data-heavy sectors such as cloud computing, entertainment, and scientific research.
The Road Ahead
Holographic storage is undeniably an exciting prospect. However, it is still in the research and development phase, and practical, commercial applications are yet to be unveiled. Challenges such as the need for precise alignment and stability, high power consumption, and the cost of production need to be addressed before it becomes a mainstream data storage solution.
Nonetheless, the progress in this field is encouraging. With continued research and ongoing advancements, holographic storage may soon move out of the realm of science fiction and into our everyday lives, transforming the way we store and access data forever.