Future Trends in Green Electronics Development
The electronics industry is at a pivotal moment, with a growing emphasis on environmental responsibility. As consumers and regulators increasingly demand more sustainable products, the focus is shifting from a linear 'take-make-dispose' model to one that prioritizes ecological balance. This evolution is driving significant innovation across the entire lifecycle of electronic devices, from initial design and material sourcing to manufacturing, usage, and end-of-life management, paving the way for a greener technological future.

The global consumption of electronic devices continues to rise, bringing with it concerns about resource depletion, energy consumption, and electronic waste. In response, a transformative movement towards green electronics development is gaining momentum. This shift is not merely a trend but a fundamental re-evaluation of how technology is conceived, produced, and consumed.
What is Driving Sustainability in Electronics?
Several factors are propelling the electronics sector towards greater sustainability. Environmental impact is a primary concern, with manufacturers facing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, minimize hazardous materials, and conserve natural resources. Consumer awareness is also a significant driver; a growing segment of the market actively seeks eco-friendly gadgets and devices. Furthermore, evolving regulations worldwide are mandating higher standards for product lifecycle management, energy efficiency, and waste reduction. This confluence of environmental consciousness, market demand, and regulatory frameworks is fostering an environment ripe for innovation in green technology.
The Role of Eco-design and Materials Innovation
Eco-design is at the heart of future green electronics. This approach integrates environmental considerations into every stage of product development, aiming to minimize ecological impact from conception. Key aspects include designing for modularity, ease of disassembly, and repairability. Simultaneously, innovation in materials is crucial. Researchers are developing sustainable alternatives to traditional components, such as bioplastics, recycled metals, and conflict-free minerals. The goal is to reduce reliance on virgin resources and ensure that materials can be safely re-entered into the supply chain, significantly lowering the overall environmental footprint of new devices.
Enhancing Durability and Longevity of Devices
One of the most effective ways to reduce electronic waste is to extend the lifespan of electronic devices. Future trends in green electronics emphasize durability and longevity through robust engineering and quality components. This includes designing products that can withstand everyday wear and tear, and are resistant to obsolescence. Furthermore, the ability to repair and upgrade gadgets is becoming a central tenet of sustainable design. Companies are exploring modular designs that allow for easy replacement of individual components, such as batteries or screens, empowering consumers to maintain their devices for longer periods and reducing the need for frequent replacements.
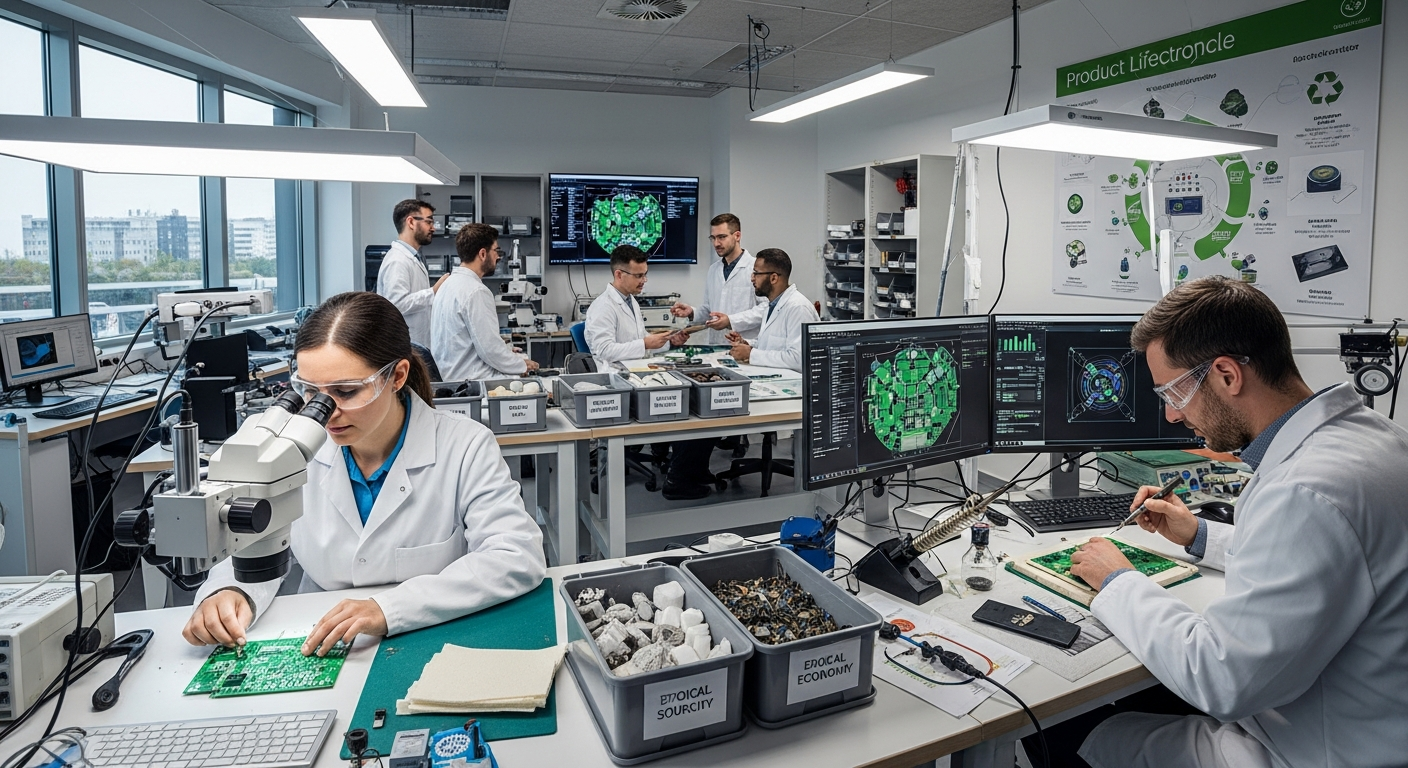
Advancements in Recycling and Circular Economy Models
The concept of a circular economy is fundamental to green electronics, aiming to keep resources in use for as long as possible. This involves robust recycling infrastructure and innovative recovery processes for valuable materials found in electronic waste. Advanced recycling technologies are emerging that can efficiently extract rare earth elements, precious metals, and other critical components from discarded devices. Beyond recycling, companies are implementing take-back programs and refurbishment initiatives, ensuring that products or their parts are reused or repurposed, thereby minimizing waste and reducing the consumption of new raw materials.
Manufacturing Efficiency and Reduced Environmental Footprint
Sustainable manufacturing practices are critical for reducing the environmental impact of electronics production. Future trends focus on optimizing efficiency across the entire manufacturing process, from raw material extraction to assembly. This includes adopting renewable energy sources for factories, minimizing water usage, and reducing hazardous emissions. Lean manufacturing principles are being applied to reduce waste generation during production. Furthermore, supply chain transparency is increasing, allowing companies to track the origin of components and ensure ethical and environmentally responsible sourcing. These efforts collectively contribute to a significantly greener and more efficient production lifecycle for electronic devices.
The future of electronics is undeniably linked to sustainability. The ongoing innovations in eco-design, materials science, manufacturing processes, and circular economy models are setting a new standard for the industry. As technology continues to advance, the commitment to developing green electronics will not only mitigate environmental challenges but also drive economic opportunities and foster a more responsible approach to consumption and waste management worldwide.