The Dynamics of Domestic Animal Care
The bond between humans and domestic animals spans thousands of years, evolving from utilitarian partnerships to deep emotional connections. Understanding the multifaceted dynamics of domestic animal care is crucial for ensuring their well-being and fostering a harmonious coexistence. This involves a comprehensive approach that considers their historical domestication, specific needs, and their intricate relationship with human society and the natural world.
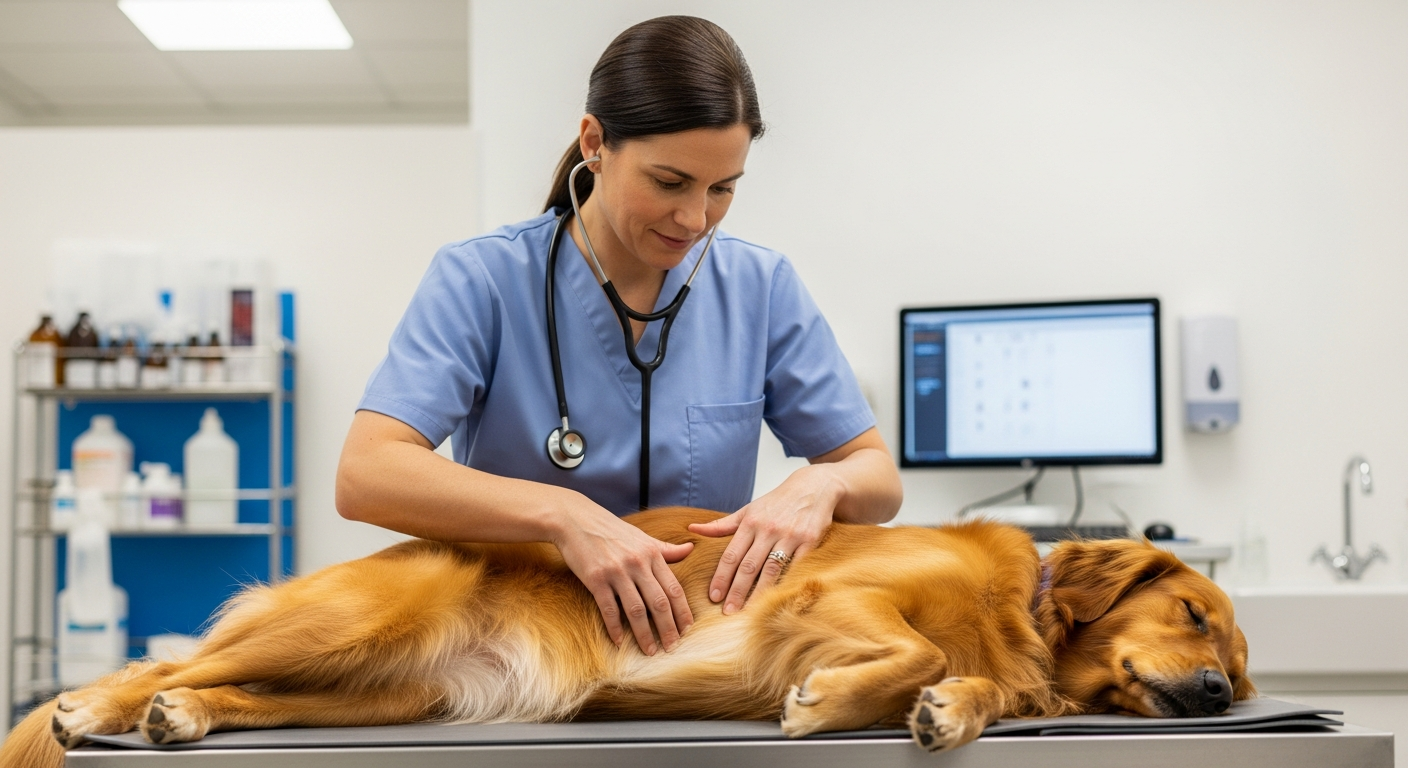

Understanding Domestication and Companion Animals
The journey of domestication began millennia ago, transforming wild species into the companion animals we know today. This process involved selective breeding for specific traits, leading to distinct breeds within various species like dogs, cats, and horses. Each species, and indeed each breed, carries unique behavioral patterns and physiological requirements shaped by this history. Recognizing these inherent characteristics is the foundation of responsible care, allowing owners to provide environments and interactions that align with their animal’s natural inclinations and evolutionary background. The role of these animals has shifted significantly, from working partners to cherished family members, highlighting the profound impact of domestication on both human and animal lives.
Essential Aspects of Animal Care and Welfare
Providing optimal care for domestic animals encompasses several key areas, all vital for their overall welfare. Nutrition stands as a cornerstone, with species-appropriate diets tailored to age, size, and activity levels being paramount for health. Regular veterinary health check-ups, vaccinations, and preventive parasite control are essential for disease prevention and early detection of issues. Training and socialization play a significant role in managing animal behavior, fostering good manners, and ensuring they can interact safely and positively with humans and other animals. Positive reinforcement methods are generally recommended for effective training, promoting a strong bond and reducing stress for the animal. Understanding an animal’s specific behavioral cues and needs helps in addressing potential problems proactively, contributing significantly to their long-term well-being and quality of life.
Creating Suitable Habitats for Domestic Animals
The environment in which a domestic animal lives profoundly impacts its health and happiness. Designing appropriate habitats involves more than just providing shelter; it means creating spaces that cater to their physical and psychological needs. For instance, dogs require secure outdoor access for exercise and mental stimulation, while cats benefit from vertical spaces and enrichment toys that mimic hunting behaviors. Climate control, safety from hazards, and access to clean water are universal requirements. The size and complexity of the habitat should be proportionate to the animal’s species, breed, and energy levels. A well-designed living space not only keeps the animal comfortable but also encourages natural behaviors, thereby preventing boredom and stress-related issues.
The Interplay with Wildlife and Ecosystems
Domestic animals, particularly those with outdoor access, can interact with local wildlife and ecosystems in various ways. Responsible pet ownership includes measures to prevent negative impacts, such as keeping cats indoors or in secure outdoor enclosures to protect local bird populations, and ensuring dogs are leashed in natural areas to prevent disturbance to native species. Proper waste disposal is also critical to prevent pollution and the spread of pathogens that could affect biodiversity. Understanding these interactions is part of a broader conservation effort, recognizing that human activities, including pet ownership, have implications for the wider natural world. Promoting responsible practices helps maintain the delicate balance of local ecosystems and protects native wildlife.
Promoting Responsible Ownership and Animal Health
Responsible ownership extends beyond daily feeding and basic care to encompass a lifelong commitment to an animal’s needs. This includes understanding the specific health predispositions of different breeds and providing regular veterinary attention throughout their life stages. Preventative care, such as dental hygiene, appropriate exercise, and mental enrichment, contributes significantly to an animal’s longevity and quality of life. Owners are also encouraged to consider microchipping their pets for identification and to spay or neuter them to help manage pet overpopulation, which has significant implications for animal welfare globally. Education on breed-specific care requirements and common health issues empowers owners to make informed decisions for their pets.
The Role of Training in Animal Behavior and Integration
Effective training is a fundamental component of domestic animal care, essential for shaping desirable behavior and facilitating harmonious integration into human households and society. Training helps establish clear communication between pets and their owners, reducing stress and confusion for both. For dogs, basic obedience commands like sit, stay, and recall are crucial for safety and control in various environments. For other animals, training might involve litter box use for cats or harness training for ferrets. Beyond basic commands, addressing specific behavioral challenges through positive reinforcement techniques can prevent issues such as excessive barking, destructive chewing, or aggression. Proper training not only enhances an animal’s quality of life by allowing them more freedom and interaction but also strengthens the bond between pet and owner, leading to a more fulfilling companionship.
Caring for domestic animals is a profound responsibility that offers immense rewards. It requires a continuous commitment to understanding their specific needs, providing appropriate care, and recognizing their place within both human society and the broader natural environment. By embracing these dynamics, owners contribute to the welfare of their pets and foster a more compassionate world for all species.